最新消息
2024.03.01
What Are Toxic Chemical Substances? Classification of Toxic Chemicals in Taiwan
What Are Toxic Chemical Substances?
Toxic chemical substances (often referred to in Chinese as 「毒化物」) are chemicals that are intentionally produced or unintentionally generated as by-products during manufacturing processes.
They typically have toxic or hazardous properties, and may:
- Harm humans, animals, or plants
- Pollute the environment
- Impair public health through single or repeated exposure
These substances can enter the human body or the environment via:
- Inhalation
- Ingestion
- Skin contact
and may cause poisoning, illness, chronic disease, or other adverse effects.
Legal Framework and Control in Taiwan
According to Taiwan's Toxic and Concerned Chemical Substances Control Act, the competent authority has officially listed 488 toxic chemical substances for regulation.
Key regulatory features include:
- Classification and quantity-based management to ensure effective control of toxic chemical substances
- Use of bans, restrictions, permits, approvals, and registration to enhance regulatory effectiveness
- Requirements to record handling and release quantities, and submit reduction plans where applicable
- For handlers of Class 1 to Class 3 toxic chemical substances, there is an obligation to establish:
- Hazard prevention plans
- Emergency response plans
- And to make relevant information available to the public
These measures aim to strengthen hazard assessment and prevention, and to reduce the risk of toxic chemical incidents.
How Are Toxic Chemical Substances Classified?
Toxic chemical substances are classified into four classes based on their properties and toxicological characteristics. Substances that meet the criteria and are formally announced by the central competent authority fall into one of the following categories:
Class 1 – Substances that are not readily decomposed (難分解物質)
These substances:
- Do not easily break down in the environment, or
- Tend to bioaccumulate, biomagnify, or undergo biotransformation,
- Leading to long-term environmental pollution or health hazards.
Examples:
- Mercury
- Benzene
- Ethylene oxide
- Formamide
Class 2 – Substances with chronic toxicity (慢毒性物質)
These substances may cause long-term or delayed health effects, such as:
- Tumor formation (carcinogenicity)
- Impaired reproductive or biological functions
- Teratogenic effects (birth defects)
- Genetic mutations
- Other chronic diseases
Examples:
- Cadmiu
- Acrylonitrile
- Formaldehyde
- Vinyl chloridem
Class 3 – Substances with acute toxicity (急毒性物質)
These substances can immediately endanger human health or biological life after short-term or high-level exposure.
Examples:
- Chlorine
- Fluorine
- Phosphine
Class 4 – Other toxic chemical substances (毒性化學物質)
Class 4 substances include those that:
- Have endocrine-disrupting properties, or
- May pollute the environment and harm human health, even if their effects differ from the typical acute or chronic toxicity of Classes 1–3.
Examples:
- Dichloromethane
- Acetaldehyde
- Diphenylamine
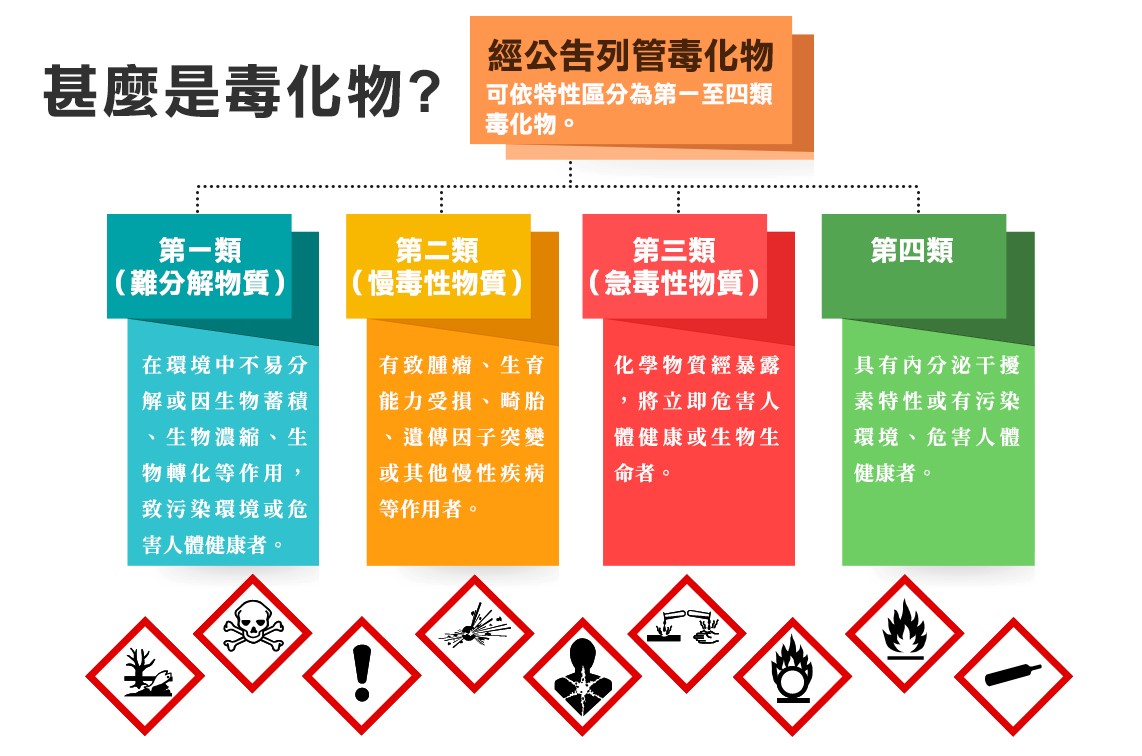
Image credit: Chemical Substance Administration, Ministry of Environment (Taiwan).